The World Health Organization (WHO) has for mandate the production of international classifications on health that constitute the International Family of Classifications. These classifications constitute a group of integrated classification products to be used alone or jointly, with the purpose of improving health through the provision of information for decision-making at all levels.
In general, the WHO Family of International Classifications aims to:
- establish a common language to improve communication
- permit comparisons of data across countries' health-care disciplines, services and time
- provide a conceptual framework of information dimensions which are related to health and health management
- serve as the framework of international standards to provide the building blocks of health information systems.
TYPES OF CLASSIFICATIONS
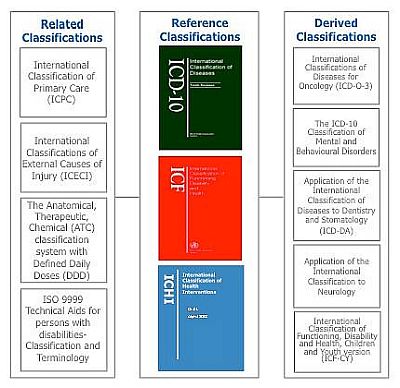
- Reference classifications are the classifications that cover the main parameters of the health system, such as death, disease, functioning, disability, health and health interventions. WHO reference classifications are a product of international agreements. They have achieved broad acceptance and official agreement for use and are approved and recommended as guidelines for international reporting on health.
- Derived classifications are based upon reference classifications. Derived classifications may be prepared either by adopting the reference classification structure and classes, providing additional detail beyond that provided by the reference classification or they may be prepared through rearrangement or aggregation of items from one or more reference classifications. Derived classifications are often tailored for use at the national or international level.
- Related classifications are those that partially refer to reference classifications, or that are associated with the reference classification at specific levels of the structure only.
The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems - 10th Revision (ICD-10) is one of the international standards most frequently used for morbidity and mortality statistics in the World.
The purpose of the ICD is to allow the systematic registration, analysis, interpretation and comparison of mortality and morbidity data collected in different countries or areas, at different times. The classification converts diagnostic terms and other health problems from words to alphanumeric codes so they can be stored and later retrieved for analysis.
| Volume 1 of the ICD | Training resources | Revision of the ICD-10: ICD-11 |
|---|---|---|
|
ICD-10 Updates
2018 - Volume 1 (Spanish) | 2018 - Volume 2 (Spanish) | 2018 - Volume 3 (Spanish) | 2016 Update
The International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) is a reference classification that, along with the ICD, constitute one of the most important reference in the FIC.
The ICF constitutes an innovating classification by widening the application of the FIC to information on functioning and disability at the individual and population levels, in order to generate evidence for the planning of services, evaluation of public health interventions, programs, and policies in the countries.
In order to promote the development, implementation, dissemination, and adequate use of the FIC in National Health Information Systems, WHO relies on support from Collaborating Centers that, along with Regional Offices, are part of the WHO-FIC Network.
The use of international classifications in health information systems requires an adequate knowledge of its contents and of the process to integrate the data in the system.
The adequate application of the international classifications in required in various stages of the process, including the collection, processing, capture, validation, presentation, analysis, and dissemination of the information.
