At PAHO, we aim to end more than 30 diseases and related conditions by 2030. The Elimination Initiative is an innovative policy that promotes an integrated, sustainable approach to accelerate progress towards elimination in the Region of the Americas.
Our commitment to the Elimination Initiative is to improve the quality of life for people and communities. This requires us to think and act differently, creating synergies and transformative strategies. Take action to end the suffering and harm caused by communicable diseases, ensuring health thrives and communities flourish.
Why Now?
The timing is critical. Over the past decades, the Americas have achieved remarkable milestones in disease elimination. Smallpox was eradicated in 1980, followed by the elimination of polio. Rubella, congenital rubella syndrome, and neonatal tetanus were also wiped out. By 2024, several countries had become malaria-free, and mother-to-child transmission of HIV had been halted. However, challenges persist. The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted health interventions and set back progress. Now, we must seize this moment to accelerate disease elimination and build on our successes.
Why Invest? Because It Pays Off!
According to global estimates, investing in disease elimination boosts well-being and the economy:
1. Neglected Infectious Diseases:
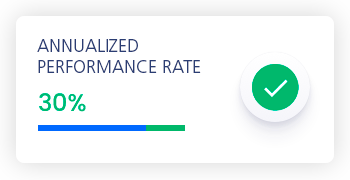
For every dollar invested in eliminating these diseases, there is a net benefit of around US$25. That’s a 30% annualized rate of return—a financial win for global health.
2. Socioeconomic Impact:
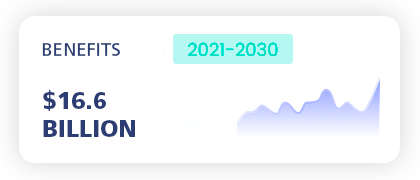
Eliminating leprosy, leishmaniasis, and Chagas disease isn’t just about health; it’s about economics. We’re talking $16.6 billion in benefits for 2021-2030, plus $10.4 billion less in out-of-pocket expenses.
3. Tuberculosis:
Invest in diagnosis and treatment, and the returns range from US$30 to as high as US$115 per dollar. It’s a smart move.
4. Ending HIV:
Meeting HIV targets saves US$24 billion in treatment costs . That’s a 15-fold return on investment. Lives transformed; economies boosted.
5. Vaccination Magic:
Every dollar invested in vaccination delivers a return of US$26.35. Protecting lives, enhancing productivity—it’s a no-brainer.
Highlights
Our steadfast commitment has a profound impact across the entire Region
A history of Diseases Elimination successes
Recent certifications and validations
The results of this initiative are milestones that have significantly improved the quality of life for individuals and communities. The commitment of countries, communities, partners, donors, allies, and PAHO is reflected in these achievements.
Mother-to-child transmission of HIV and syphilis
Countries certified free of mother-to-child transmission of HIV and syphilis
Elimination targets for 2030
Communicable diseases and related conditions candidates for elimination by 2030
Elimination target
50% reduction of bacterial meningitis cases.
70% reduction of deaths due to bacterial meningitis.
Elimination target
<4 new cases per 100,000 women.
Elimination target
0% (alloctonous vectors); <=1% (autochthonous vectors) households with intra and peridomiciliary vector infestation of T.cruzi sustained for at least five (5) years in the entire territory and by all vectors.
0% (alloctonous vectors); <=1% (autochthonous vectors) households with intra and peridomiciliary vector infestation of T.cruzi either by territory or by vector in a given period.
Elimination target
Absence of community transmission of epidemic Vibrio cholerae for at least three (3) consecutive years.
Elimination target
≥90% of newborns with T. cruzi infection, cured.
Elimination target
≤ than 0.5 new cases of mother-to-child transmission of syphilis per 1,000 live births.
Elimination target
Zero (0) cases in people <15 years old per 100,000 people <15 years old.
Elimination target
≤5% of cases of fascioliasis in humans detected by coprology (sustained over time).
Zero (0) cases cases of fascioliasis in children aged 5-14 years with ≥ 400 eggs per gram of feces.
Elimination target
<2% Prevalence of moderate and severe infection due to A. lumbricoides, T. trichiura and hookworms in school-age children (5 to 14 years).
Elimination target
90% reduction in the incidence of hepatitis B compared to 2015.
<4 per 100,000 inhabitants (65% reduction in mortality from hepatitis B compared to 2015).
Elimination target
<5 per 100,000 inhabitants (90% reduction in the incidence of chronic hepatitis C compared to 2015)
<2 per 100,000 inhabitants for hepatitis (65% reduction in mortality from hepatitis C compared to 2015).
Elimination target
≤0.1% prevalence of HBsAg in children aged 4 to 6 years.
Elimination target
≤2% incidence rate of mother-to-child transmission per 100 live births of women with HIV.
Elimination target
65% reduction in annual HIV-related deaths compared to 2010 values.
<0.02 new infections per 1000 inhabitants per year (90% reduction since 2010).
Elimination target
Zero (0) human deaths from dog-transmitted rabies for five (5) consecutive years.
Elimination target
Zero (0) new autochthonous cases for at least three (3) consecutive years AFTER reaching interruption of transmission among children <15 years (indicator of disease elimination).
Zero (0) new autochthonous cases of leprosy for at least five (5) consecutive years (indicator of interruption of transmission).
Elimination target
Prevalence of microfilaremia <1% or prevalence of antigenemia <2% in persons => 5 years of age sustained for at least 4 years after stopping mass drug administration.
Elimination target
Zero (0) new autochthonous cases for three (3) consecutive years.
Elimination target
< 0.1% prevalence of infective flies and Seroprevalence of onchocerciasis in children under 10 years of age.
Elimination target
Zero (0) new confirmed cases of plague
Elimination target
90% reduction in new syphilis and gonorrhea infections compared to 2020.
Elimination target
<1% proportion of high-intensity Schistosoma mansoni infections in school-aged children (5 to 14 years).
Elimination target
<5% of trachomatous inflammation-follicular in children aged 1-9 years.
<0.2% of trachomatous trichiasis in people aged 15 years and above.
Elimination target
Pre-elimination of tuberculosis: <1 cases per 100,000 inhabitants; elimination of tuberculosis as a public health problem: <0.1 case per 100,000 inhabitants.
Elimination of environmental risk factors
Elimination target
95% reduction in the number of people practicing open defecation (2030 vs. 2020).
Elimination target
<5% percentage of population that depends on the use of polluting fuels in the household.
Maintain the Elimination
Elimination target
Zero (0) endemic cases of congenital rubella syndrome in 12 months in any defined geographical area.
Elimination target
Zero (0) endemic cases of measles in 12 months in any defined geographical area.
Elimination target
<1 new confirmed cases of neonatal tetanus per 1,000 live births in each district (or equivalent administrative unit) of a country in a year.
Elimination target
Zero (0) cases of poliomyelitis due to wild poliovirus or circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus in children younger than 15 years in 12 months in any defined geographical area.
Elimination target
Zero (0) endemic cases of rubella in 12 months in any defined geographical area.
Elimination target
Zero (0) cases of urban yellow fever due to transmission by Aedes aegypti.
Eradication
Elimination target
Zero (0) cases in the absence of vaccination in countries free of foot-and-mouth disease.
Elimination target
Absence of cases verified by PCR Zero (0) new serologically confirmed autochthonous cases for three (3) consecutive years