News




Digital Transformation Toolkit
The IS4H digital transformation toolkit was created with the aim of offering managerial, technical, knowledge, communication, and academic resources to all those health professionals, decision-makers, and institutions dedicated to strengthening health information systems, with the vision of achieving universal access to health and universal health coverage in the Region through access to good quality data, strategic information, and digital health tools for decision-making and well-being.

New Toolkit: Artificial Intelligence in Public Health

Q&A: Artificial Intelligence for Public Health Action

Knowledge Capsule: AI in Public Health Explained

The Digital Transformation in Nursing Education and Practice

Toolkit for the Digital Transformation of the Health Sector (Available in 4 Languages)

Assessment Tool for Telemedicine Readiness in Health Institutions
IS4H Basics
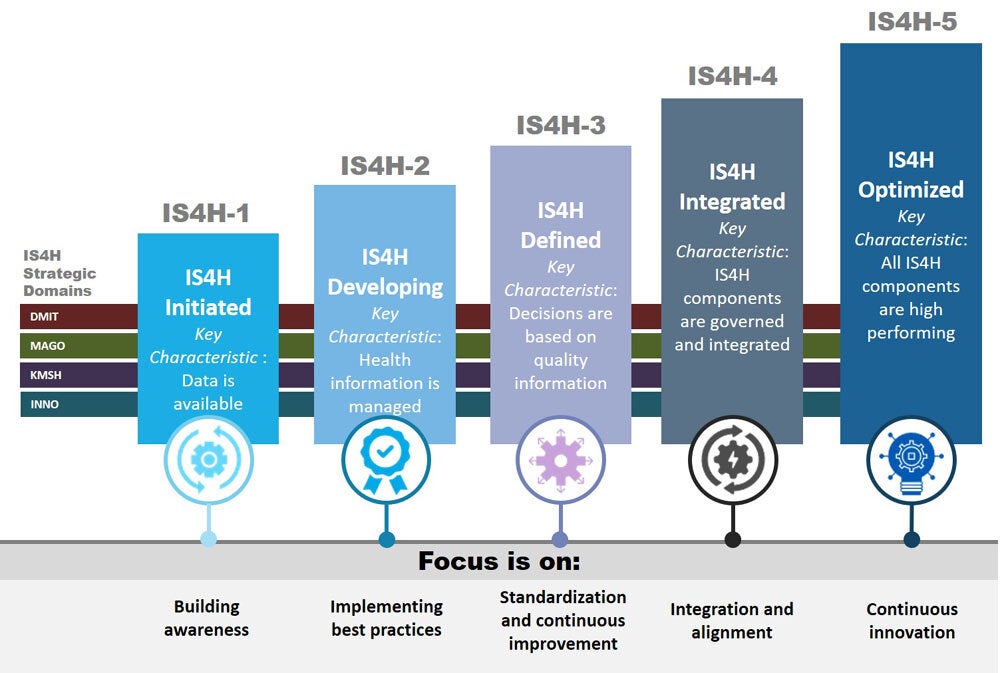
The IS4H Initiative -Maturity Model
The IS4H-MM is a reference framework guiding Information Systems for Health to keep walking along the path of change marked by the information and knowledge revolution, and shows how countries and organizations grow in capabilities to operate, interact and benefit from them. The Health Information System Maturity Model (IS4H-MM) is a framework that guides health information systems along the path for change marked out by the information and knowledge revolution, and shows how countries and organizations can increase their capacity to operate, interact with, and benefit from these systems. Read more...
The following diagram illustrates the five levels of maturity.
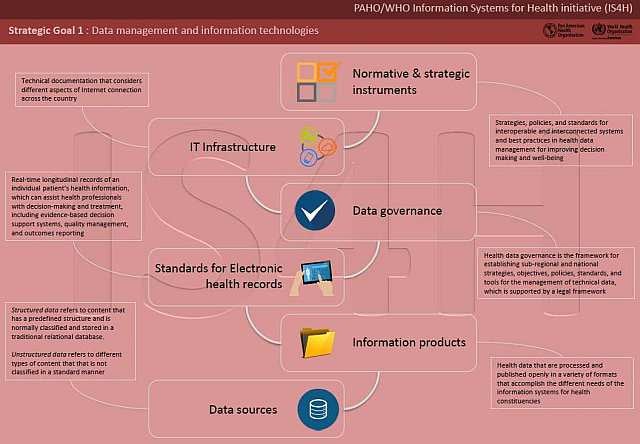
IS4H Strategic Goals
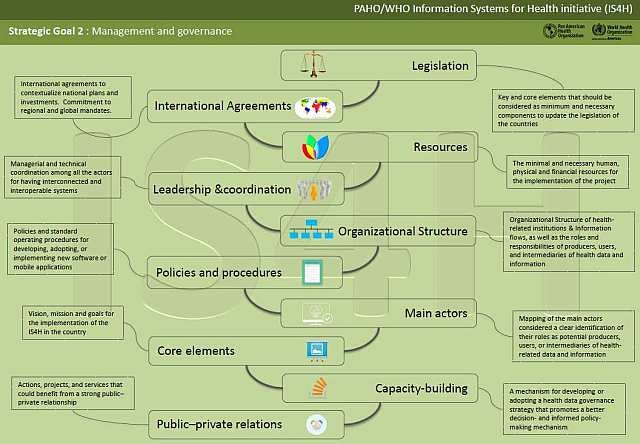
Goal 2 - Management and governance
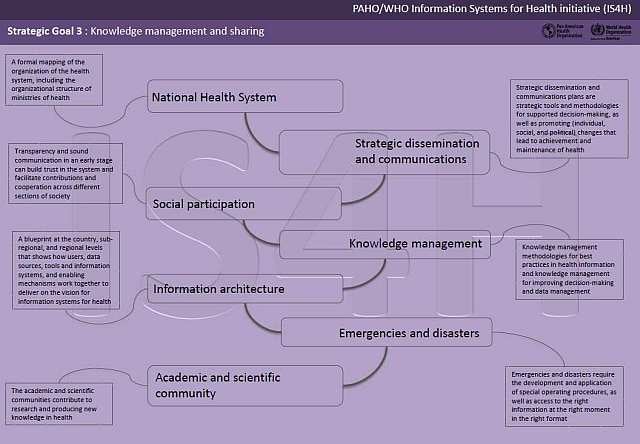
Goal 3 - Knowledge management and sharing
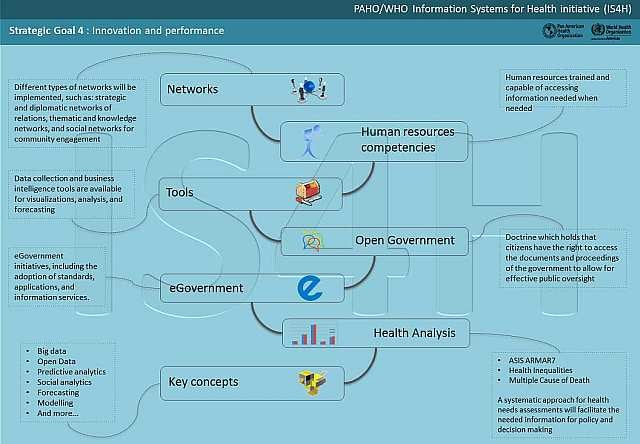
Goal 4 - Innovation and performance