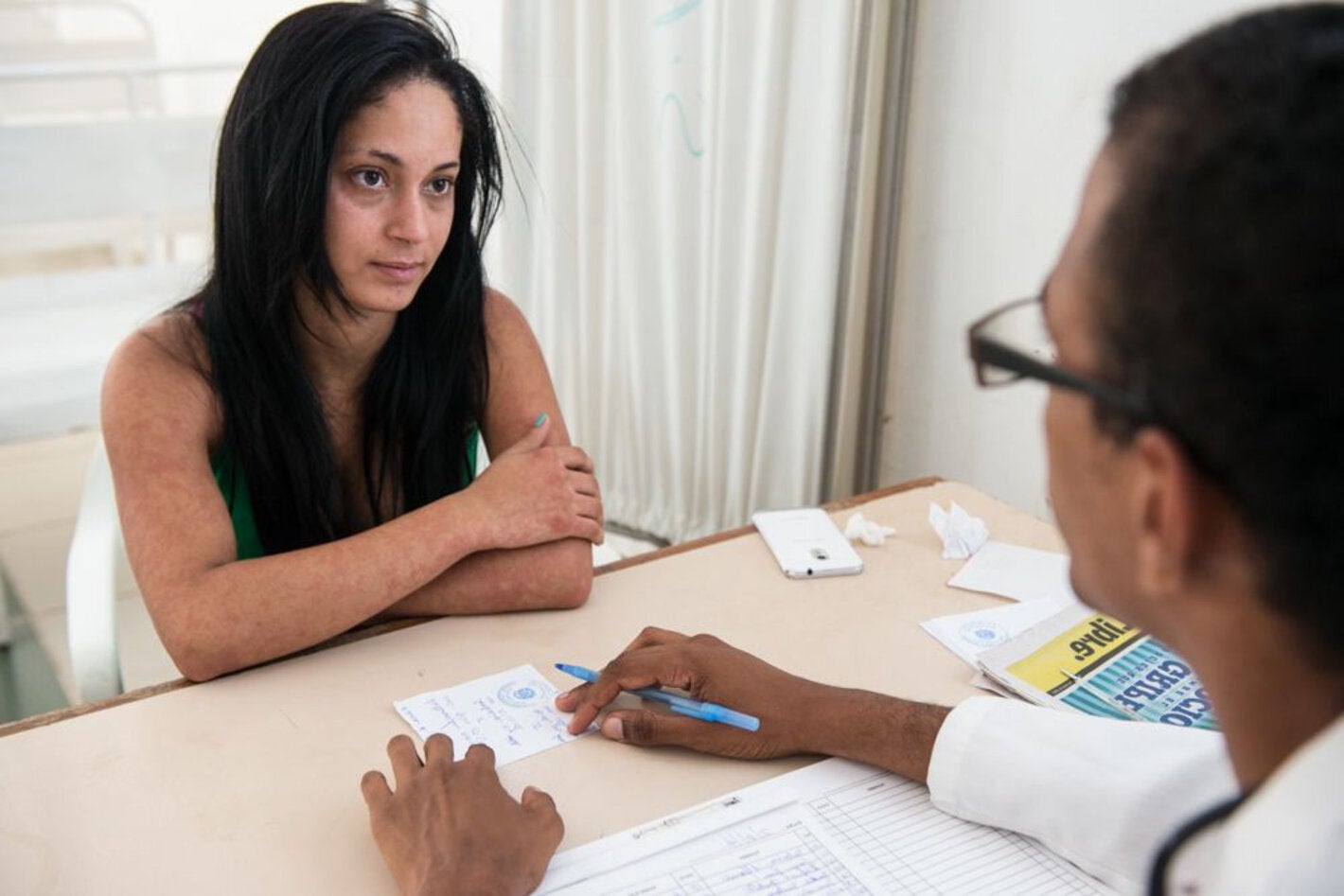
Washington, DC, February 15, 2023 (PAHO) - The Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) has called on countries of the Americas to strengthen measures to diagnose and manage chikungunya due to an increase in cases in some areas, higher numbers of susceptible persons and the start of peak transmission season in the Southern Cone.
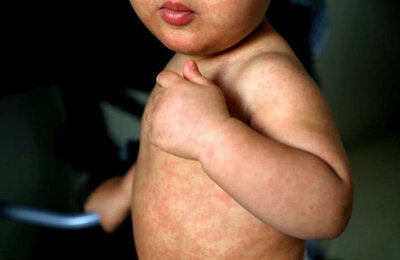
Chikungunya fever is transmitted by the Aedes mosquito, which is also responsible for spreading dengue and Zika. It can cause high fever, joint and muscle pain, and headache. There is no approved vaccine or specific treatment for the disease. On rare occasions, it can cause severe symptoms and lead to death, mainly in pregnant women, children under the age of one, older adults and people with comorbidities.
According to the PAHO epidemiological alert published on February 13, in 2021 there were over 137,000 reported cases and 12 deaths due to the disease, but in 2022 cases almost doubled, and 95 deaths were reported in 13 countries and territories of the region, the vast majority in Brazil. In the first four weeks of 2023, 30,707 cases of chikungunya were reported – 70% of which in Paraguay – as well as 14 deaths.
PAHO has urged Member States to continue strengthening surveillance, triage, diagnosis and the timely and appropriate treatment chikungunya and other mosquito-borne disease cases.
In the alert, the Organization also called on countries to step up health service capacity and preparedness, including drawing up plans for screening and reorganizing services in case of outbreaks, and strengthening care networks.
The surveillance guidelines include recommendations on appropriate sampling and laboratory algorithms for diagnostic confirmation by molecular testing (RT-PCR), considering differential diagnosis with other pathologies.
PAHO also recommend that specific care be provided to patients at different levels of care and stages of infection, which may require training of health personnel in diagnosis and case management.
The best protection against chikungunya is to avoid mosquito bites. The main method of reducing transmission is to mobilize communities to reduce and eliminate mosquito breeding sites. If chikungunya infection is suspected, it is recommended that persons seek immediate assistance at a health clinic.