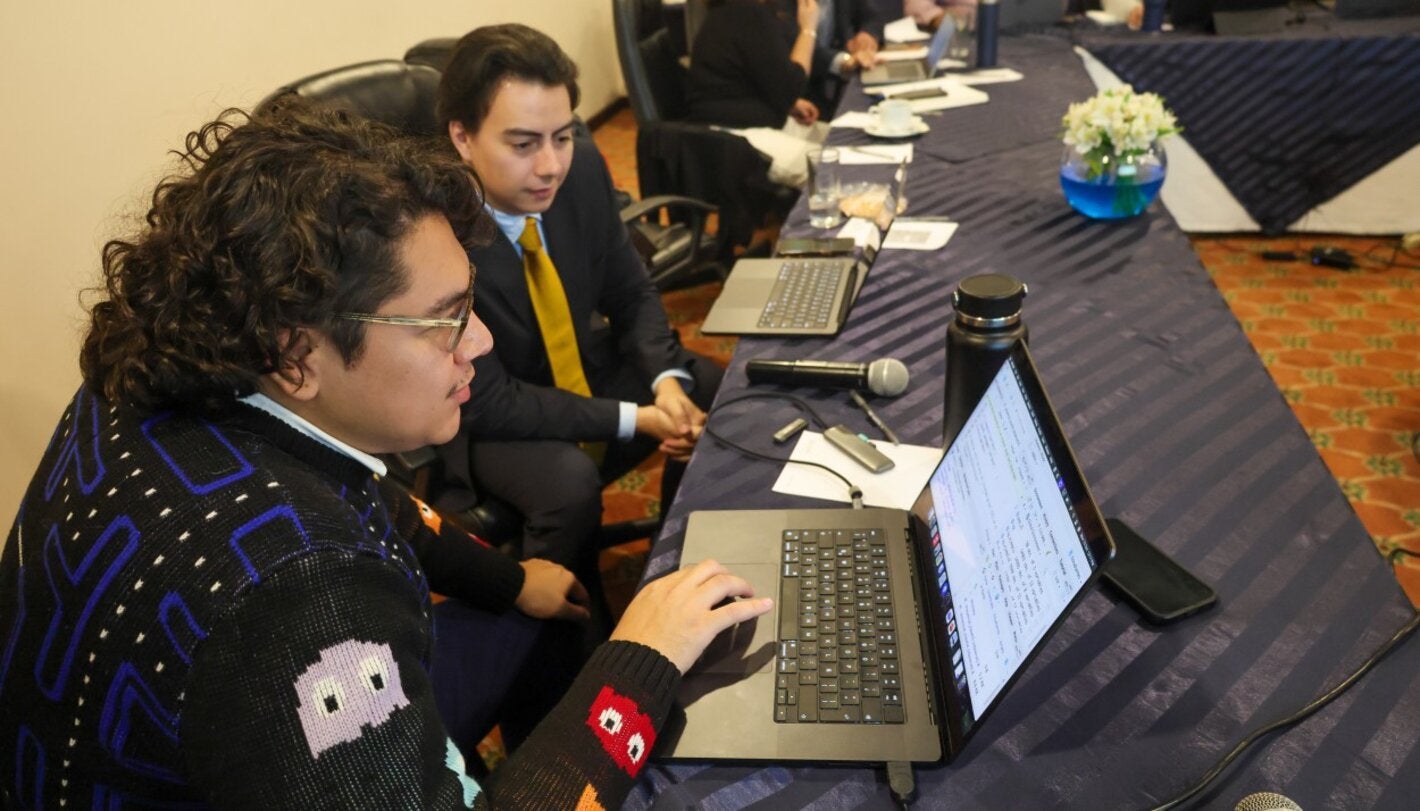
Ciudad de Guatemala, November 20, 2025 (PAHO/WHO) - The Pan American Health Organization/World Health Organization (PAHO/WHO), through the Health Emergencies and Risk Assessment Information Unit (HIM) of the Department of Emergencies (PHE), developed training in data analysis using R Software during October and November as part of strengthening national capacities for epidemiological surveillance, risk assessment, and timely response to public health emergencies.
Strengthening data analysis has been identified as a strategic component for improving health emergency management in the Region of the Americas, where the availability of reliable, reproducible, and timely information is crucial for designing effective interventions. In this context, R software—an open source, statistical programming language—enables the development of advanced analytical models, the automation of workflows, the integration of diverse data sources, and the generation of reproducible visualizations, thereby promoting evidence-based decision-making.
The objective of the training was to improve the analytical skills of technical teams through the use of essential tools and packages for data processing, standardization of analysis routines, and preparation of epidemiological bulletins, which facilitate decision-making during public health events.
The course combined virtual sessions and a week of in-person work, where participants developed applied exercises using real data. As a final assessment, each team prepared a reproducible epidemiological report based on their own databases, applying the analysis, visualization, and automation methods acquired during the training.
The training process was aimed at professionals from the Directorate of Epidemiology and Risk Management of the Ministry of Public Health and Social Assistance (MSPAS) and epidemiologists at the subnational level, who play a key role in the surveillance and early detection of public health events. In addition to strengthening their technical capacities, participants are prepared to act as institutional replicators, facilitating the adoption of R software within the national system and contributing to the construction of a standardized and sustainable data analysis culture.
This initiative is part of PAHO/WHO's efforts to support Member States in implementing advanced analytical tools, strengthening health information systems, and promoting the use of reproducible methodologies that favor interoperability and timely analysis during emergencies. As part of the next phases, PAHO/WHO will continue to provide technical support for the development of specific analytical routines, the automation of information flows, and the integration of capacities in the units responsible for epidemiological surveillance and analysis in Guatemala.