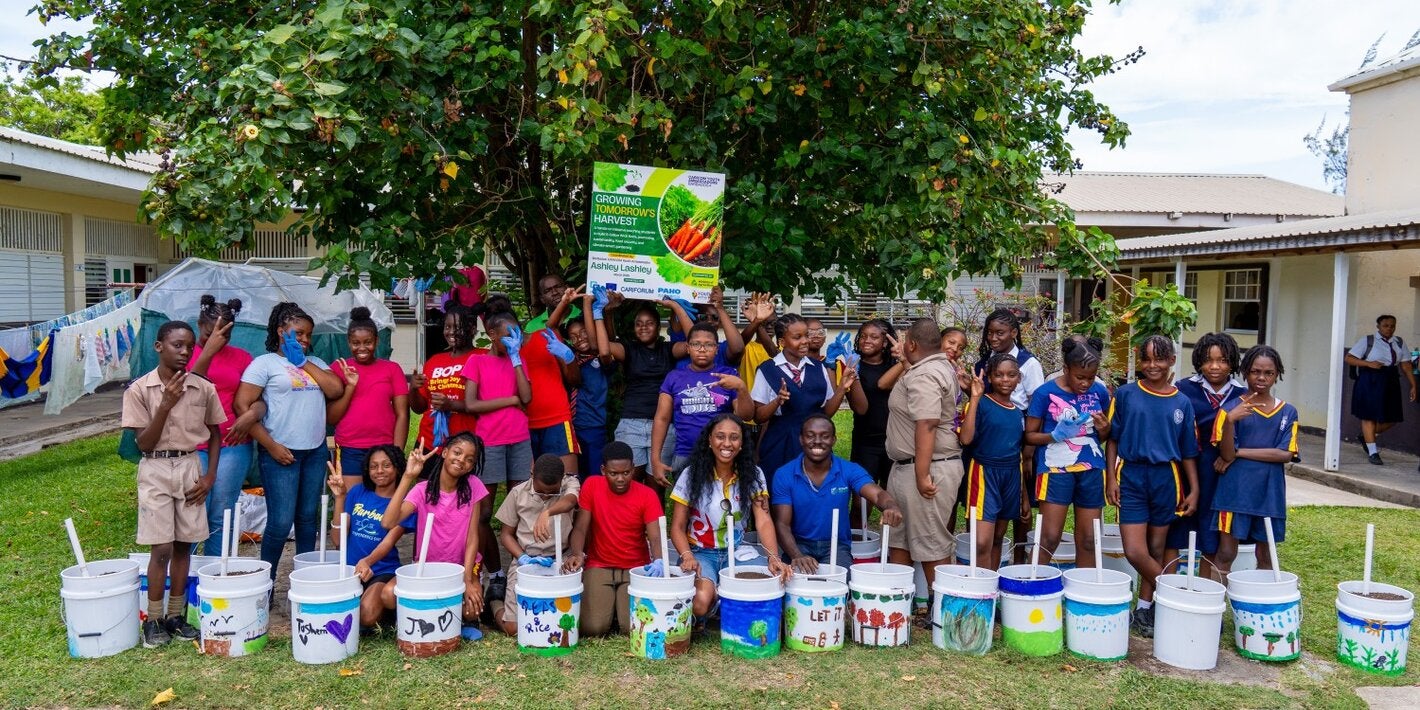
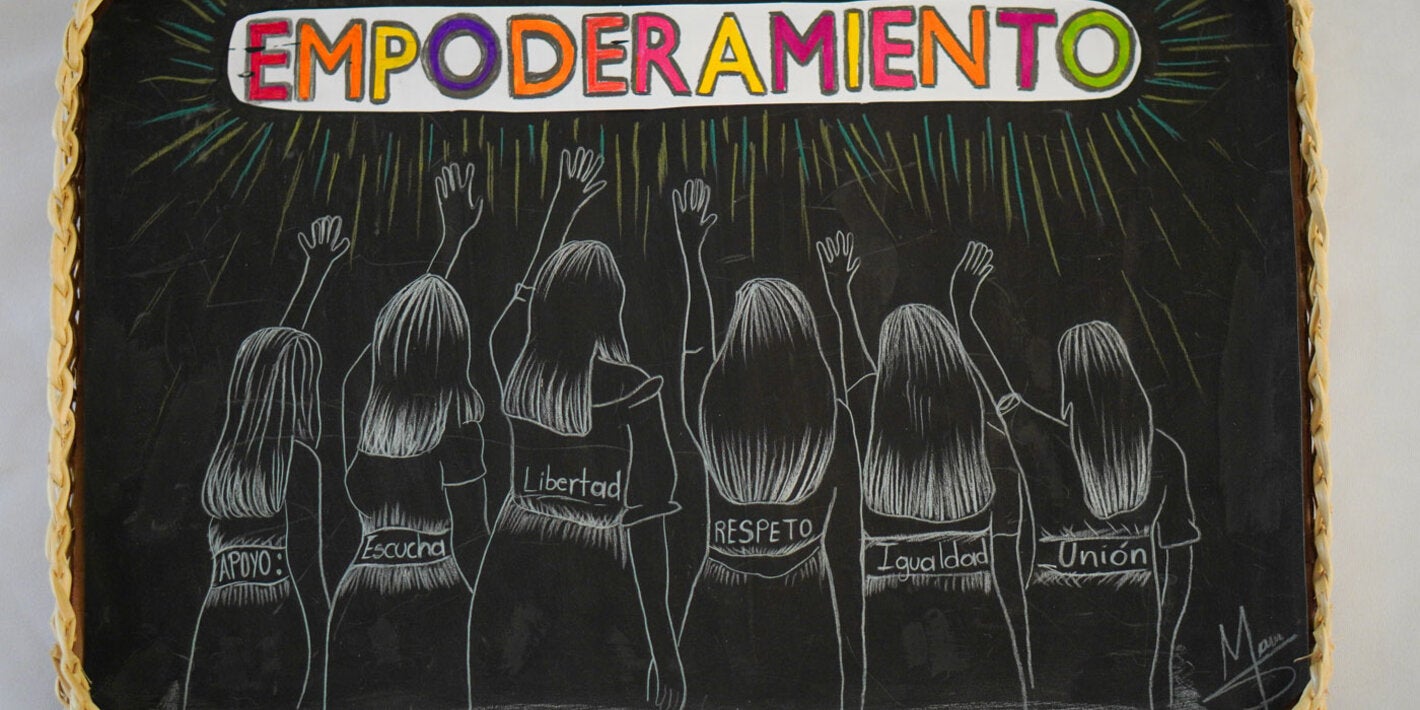
Young people are a sizable age group, comprising approximately 30% of the population in Latin America and the Caribbean. Adolescents are generally considered to be a "healthy" segment of the population, and their health needs are often overlooked. However, investing in health and education for young people and the alignment of economic policies enable productivity and economic growth.
Furthermore, investment in young people's health is essential to protect investments made in childhood (e.g. significant investments in vaccines and food programs) and secures the health of the future adult population. Most habits detrimental to health are acquired during adolescence and youth and manifest themselves as health problems in adulthood (e.g. lung cancer caused by the consumption of tobacco), adding an avoidable financial burden to the health systems.
- Youth violence is a global public health problem. It includes a range of acts from bullying and physical fighting, to more severe sexual and physical assault to homicide.
- Promoting healthy behavior during adolescence, and taking steps to better protect young people from health risks are critical for the prevention of health problems in adulthood, and for countries' future health and ability to develop and thrive.
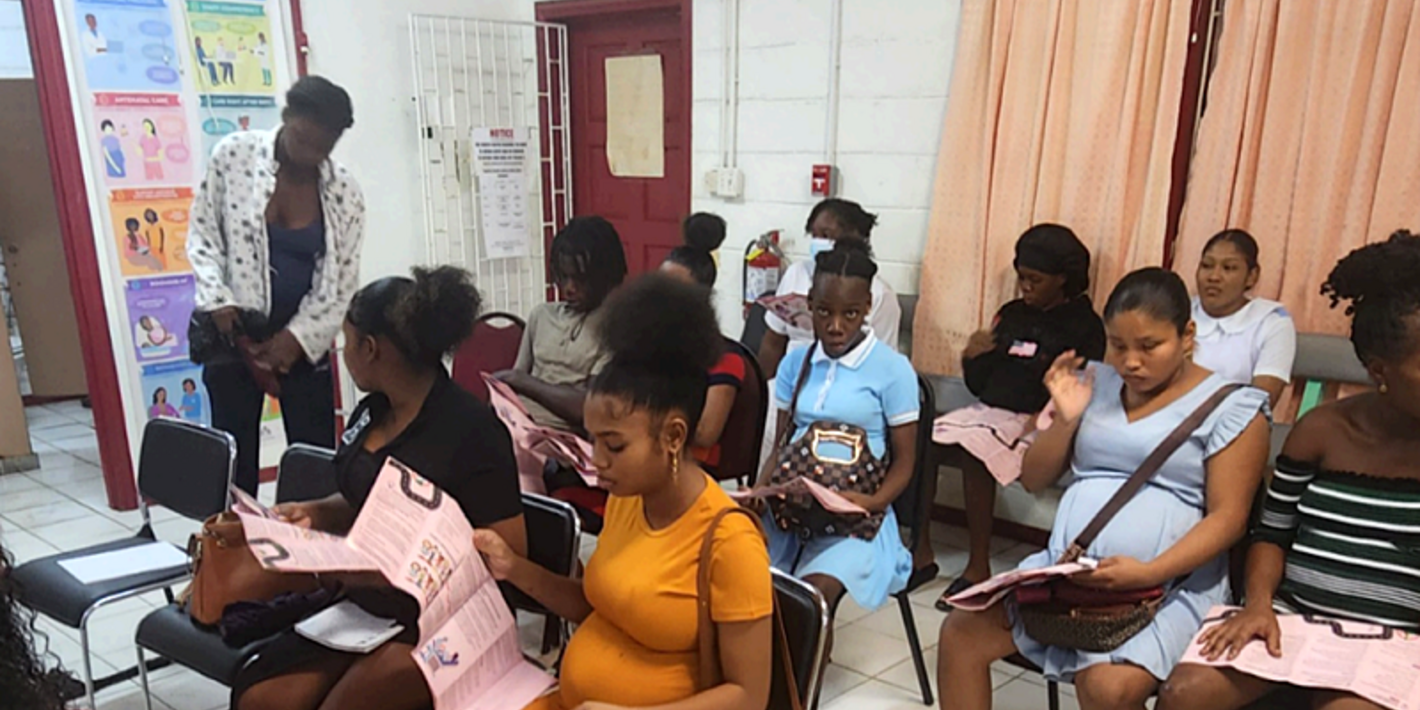
- Adolescent pregnancies are a global problem that occurs in high, middle, and low income countries. Around the world, adolescent pregnancies are more likely to occur in marginalized communities, commonly driven by poverty and lack of education and employment opportunities
Over the past years, the Region of the Americas has made important progress toward improving the health of women, children, and adolescents. Neonatal, child, and maternal mortality have declined. However, the advancements have not benefitted all population groups equally: major variances exist between and within countries.
Consistently, women and children from the lower socio-economic levels, along with those living in rural settings, indigenous groups, Afro-descendants, and the less educated have higher burdens of morbidity and mortality. Adolescent mortality, mainly due to preventable causes, has remained stagnant or has increased, and adolescent pregnancy remains unacceptably high.
In September 2018, Member States of the Pan American Health Organization adopted the Plan of Action for Women’s, Children’s and Adolescents’ Health 2018-2030. This Plan of Action is based on four complementary and mutually reinforcing strategic lines of action:
- Strengthen a transformative policy environment to reduce health inequities among women, children, and adolescents.
- Promote universal, effective, and equitable health and well-being for all women, children, and adolescents in their families, schools, and communities throughout the life course.
- Expand equitable access to comprehensive, integrated, quality health services for women, children, adolescents, and families, that are people-, family-, and community-centered.
- Strengthen information systems for the collection, availability, accessibility, quality, and dissemination of strategic information, including health data and statistics on the health of women, children and adolescents, within the framework of the principles proposed in this Plan.
Within this Plan of Action, the role of the Pan American Health Organization is to:
- provide technical cooperation to Member States for the development of updated national action plans and to disseminate tools that facilitate integrated, equity-based, and innovative approaches to the health of women, children, and adolescents;
- strengthen coordination of the Plan of Action with similar initiatives developed by other international technical and financial agencies and global initiatives for the health and well-being of women, children, and adolescents;
- report periodically to the Governing Bodies on the progress made and challenges faced in implementation of the Plan of Action.