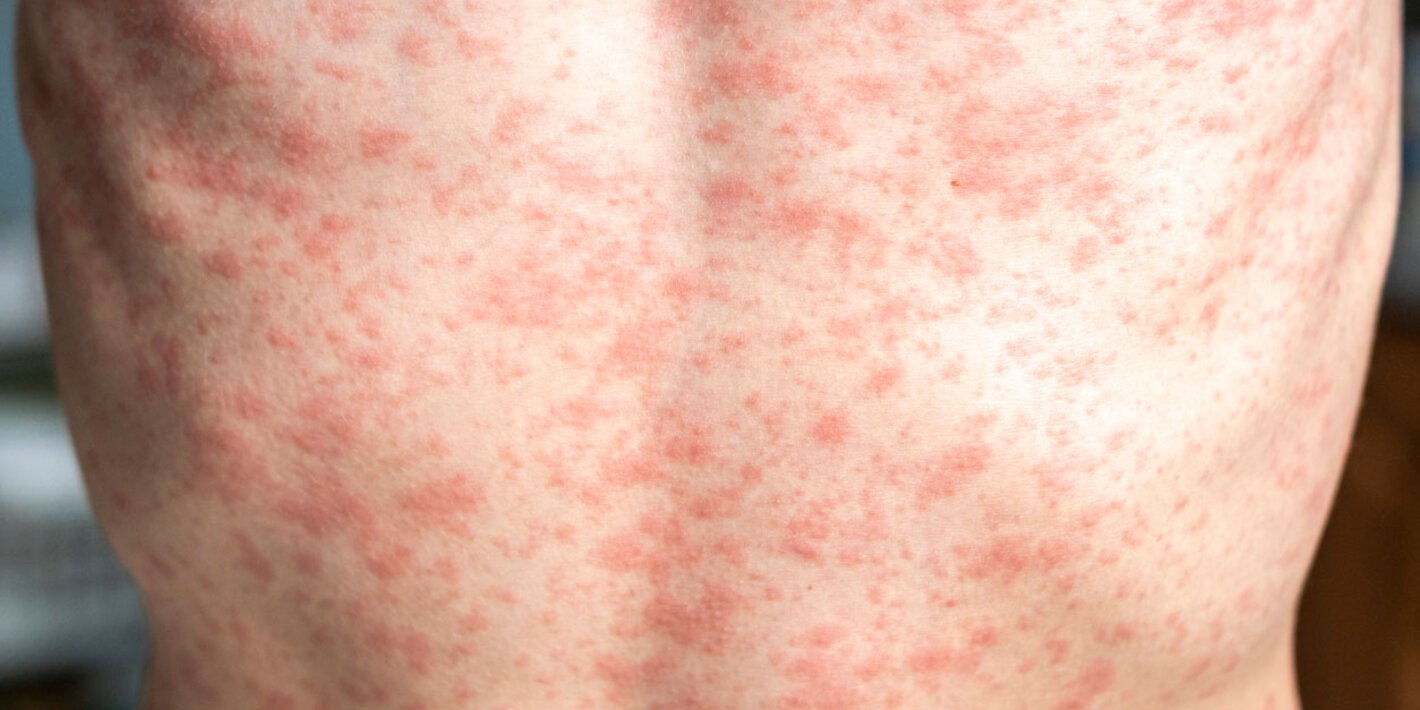
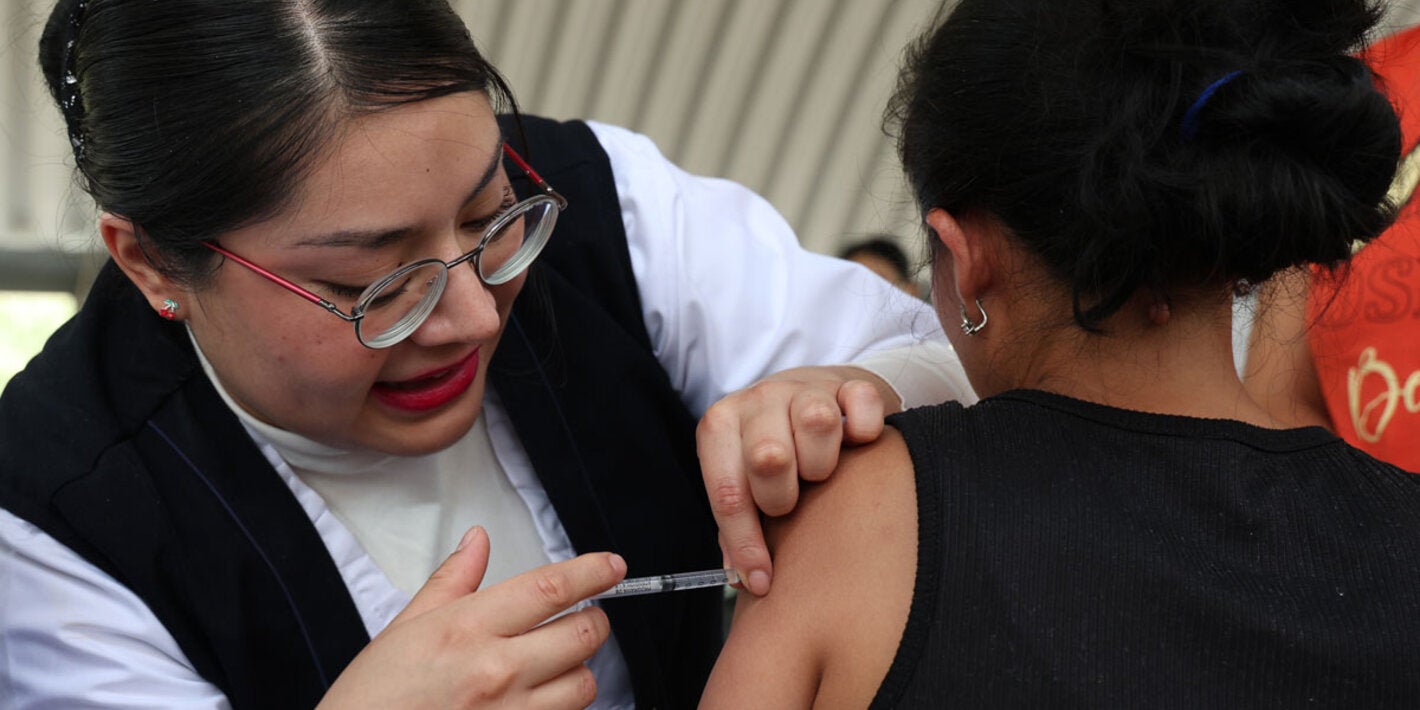
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease, which affects mostly children. It is transmitted via droplets from the nose, mouth, or throat of infected persons. Initial symptoms, which usually appear 10-12 days after infection, include high fever, runny nose, bloodshot eyes, and tiny white spots on the inside of the mouth. Several days later, a rash develops, starting on the face and upper neck and gradually spreading downwards. There is no specific treatment for measles and most people recover within 2-3 weeks. However, particularly in malnourished children and people with reduced immunity, measles can cause serious complications, including blindness, encephalitis, severe diarrhea, ear infection, and pneumonia. Measles can be prevented by immunization.
| In 2025, 14,975 confirmed measles cases were reported in 13 countries, a 32-fold increase compared to 2024. | |
| Between 2000 and 2023, the measles vaccine alone prevented 6.2 millions deaths in the Americas, and 93.7 million worldwide since 1974. | |
| Measles immunization in 94 low and middle income countries yielded a return of US$ 76.5 for every US$ 1 invested in vaccination. | |
| Between 2000 and 2023, the global mortality rate declined by 83%, thanks in part to measles vaccination activities. | |
| It is estimated that measles vaccines helped prevent 60 million deaths between 2000 and 2023 worldwide. |
Featured video
- Measles is a very contagious viral disease that especially affects children and can cause severe health problems, including severe diarrhea, ear infections, blindness, pneumonia, and encephalitis (swelling of the brain). Some of these complications can lead to death.
- At the global level, measles continues to be one of the leading causes of death among young children, despite the fact that there is a safe and effective vaccine to prevent it. There is no specific antiviral treatment against the measles virus.
- Serious cases are especially frequent in malnourished young children, especially those whose immune systems are weakened. In populations with high levels of malnutrition and inadequate health care, measles can kill in up to 10% of cases.
- Measles is transmitted by airborne droplets from the nose, mouth, or throat of an infected person. The virus can stay active and contagious in the air or on surfaces for two hours.
- Symptoms tend to be high fever, runny nose, cough, red and watery eyes, small white spots on the inside of the cheeks, and widespread rash all over the body.
- Before widespread vaccination began in 1980, measles caused 2.6 million deaths a year throughout the world, 12,000 of them in the Americas.
- Between 1970 and 1979, Latin American countries reported about 220,000 cases of measles a year.