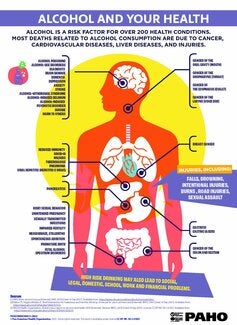
The harmful consumption of alcohol is associated with a range of health and social consequences, including injuries, several forms of cancer, chronic liver disease, heart disease, alcohol dependence, and domestic violence.
Priority cross-cutting issues for the program include gender, human rights, health promotion and services in primary health care.
- Alcohol was responsible for 5.5% of all deaths in the Americas, and 6.7% of all disability-adjusted life years.
- 54% of the total population are current drinkers, 29% are life abstainers, and 17% are former drinkers.
- Fewer people are drinking now, but those who do are drinking more.
- Annual per capita consumption among people over 15 years of age was 8.0 liters.
- Annual per capita consumption among DRINKERS was 15.1 liters
- On average, each drinker has 2.3 drinks* every day of the year. Among male drinkers, the average is 4.3 drinks daily. Among women, it is 1.4 drinks per day every day of the year.
- 40.5% of all current drinkers are HEAVY EPISODIC DRINKERS (they drink at least 5 drinks per occasion at least monthly).
- 21.3% of the total population over 15 years old are heavy episodic drinkers.
- 18.3% of adolescents aged 15-19 years are heavy episodic drinkers.
- 8.2% of the general population over 15 years old has an ALCOHOL USE DISORDER:
- 5.1% of women >>> THE HIGHEST PREVALENCE IN THE WORLD (COMPARED TO ALL OTHER WHO REGIONS)
- 11.5% of men>>> THE SECOND HIGHEST PREVALENCE IN THE WORLD (HIGHEST IS IN THE EUROPEAN REGION)
*One standard drink is 10 grams of pure alcohol, equivalent to 250 ml of beer, 230 ml of cider, 100 ml of wine or 31 ml of distilled spirits.
Explore the data interactively in the ENLACE portal
Alcohol is causally linked to over 200 health conditions, including liver diseases, road injuries, violence, cancers, cardiovascular diseases, suicides, tuberculosis, and HIV/AIDS.
Alcohol's impact is detrimental in every country in the Region; the less developed a country is, the higher the relative burden of alcohol. But where consumption is highest, the burden of disease and injury is heaviest.
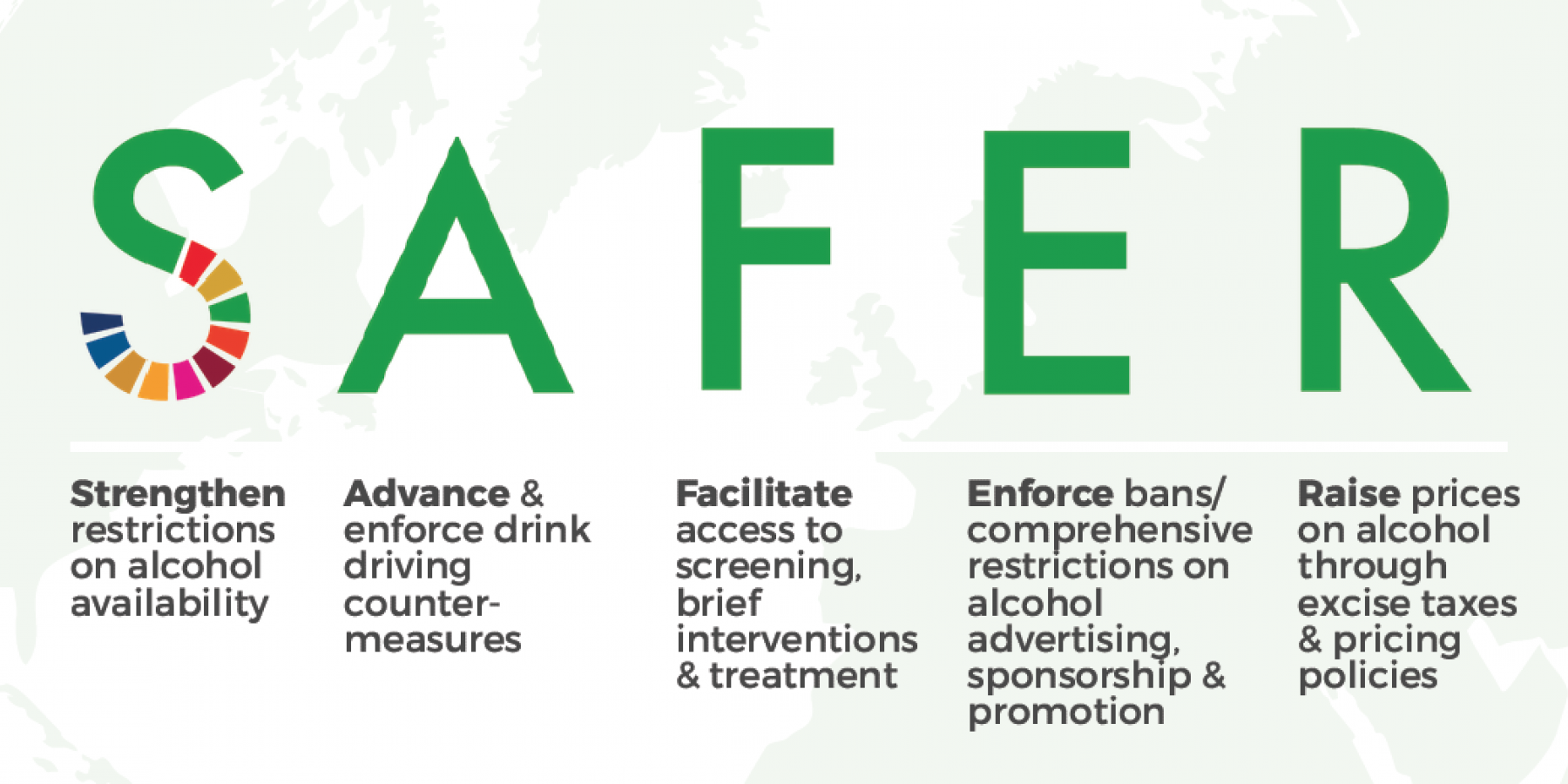
The Region of the Americas ranks as the second-highest in consumption and in the burden of alcohol, after the European Region. Alcohol consumption is expected to increase if the most effective policies are not implemented.
Learn about the impact of alcohol use on different aspects of health on the Alcohol and Health fact sheets series:
The alcohol program provides leadership and technical cooperation to Member States on public health policies related to alcohol consumption. Therefore, it generates and disseminates information on alcohol, evidence-based policies and interventions, and monitors trends in consumption and related problems, with the goal of minimizing the negative health outcomes associated with their use.
Among the various psychoactive substances consumed in the region, alcohol is a leading risk factor for the burden of disease.